Why Constellation $Dag is a Unicorn 🦄
This is going to be a pretty long blog post. The first part, which is the part you’re reading right now, is mostly ramblings. You can skip this part but we highly recommend to just let your eyes glide over the entire post.
We didn’t stumble upon this unicorn by luck and want to show you our thought process so you have more tools to judge it yourself.
There’s a specific reason why this post is going to be way longer than probably anything we’ll create on this website.
Being in the cryptocurrency space for so many years gave us a lot of time to research many different coins and tokens.
I went to Coinmarketcap and at this point in time there are over 8000+ cryptocurrencies (as off november 2023) listed on there. I don’t need to tell you that a lot of them are 💩. Some of them don’t even have a functioning website connected to it.
Then there are those that have a functioning website but don’t really say anything meaningful on it. No shade to the BTCboyz but they are the clear definition of an “brooo….let’s start a company brooo!”
No clear goal or direction.
Just vibes.
Maybe they’ll turn it around in the future, but at this point in time these are the type of investments we would definitely stay away from.
Putting your money in these types of investments is a easy way to come out broker on the other side.
So the reason we’re going to take our time explaining Constellation is because unlike many cryptocurrencies in the space, we truly think they’ve created something very unique.
Over the last 7-8 years in our cryptocurrency journey we’ve dissected thousands of them.
Yes, we literally clicked on thousands of links on websites like Coinmarketcap and Coingecko to see who’s creating the best of the best. A mission to find the one that does it better than the rest.
See there’s good, and there is great. In life it is important to understand the difference between good and great. Something good meets expectations while something great exceeds expectations. Being great shows a level of excellence and mastery that sets it apart. In this post we’re going to show you what sets Constellation apart.
You’ll most likely come across words you’ve never encountered before and that’s completely normal. Don’t get stuck on a single sentence or feel frustrated if you don’t understand something (yet). Just keep reading. The paragraphs in this blog post are mostly structured to introduce the difficult terms first, and then gradually make things easier to understand. This way, you’ll naturally learn what others in the space are talking about when they use certain words.
Time to dive a little deeper.
1. What is the problem that needs to be solved?
Traditional blockchains, while revolutionary, face several inherent challenges that have become more apparent as their usage has expanded. These challenges primarily revolve around scalability, speed, and energy consumption.
Scalability: One of the most significant issues with traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum is scalability. The blockchain is essentially a digital ledger of transactions, with each block in the chain containing a set of transactions.
As the number of users and transactions grows, the size of the blockchain grows as well. However, each block has a size limit, which means it can only contain a certain number of transactions. This limitation leads to a bottleneck, especially during times of high transaction volume.
For instance, Bitcoin can only handle about 7 transactions per second (tps), and Ethereum about 15-30 tps. In comparison, a global payment system like Visa can process thousands of tps. This limitation hinders the widespread adoption of blockchain for large-scale transaction processing.
Speed: The speed of transaction processing in traditional blockchains is closely tied to their scalability issues. Each transaction in a blockchain needs to be verified by network participants (nodes) and added to a block. The process of creating a new block and reaching consensus among nodes (through mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) takes time.
In Bitcoin, for example, a new block is created approximately every 10 minutes. During periods of congestion, transactions can take much longer to be confirmed, leading to delays and increased transaction fees. Yes we know there are “solutions” like Lightning network or Layer 2 scaling networks.
However, both of those come with their own set of problems. Lightning is not easy accessible and layer 2 networks are mostly centralized. They’re bandaid solutions to a huge underlying problem.
Energy Consumption: The consensus mechanisms used in many traditional blockchains, particularly Proof of Work (PoW), are highly energy-intensive. PoW requires network participants (miners) to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks.
This process requires substantial computational power and, consequently, a significant amount of electricity. The energy consumption of networks like Bitcoin has become a major environmental concern, with the network's energy usage often compared to that of entire countries.
Centralization Risks: Although blockchains are designed to be decentralized, the high costs associated with mining (in PoW systems) or running a node for a PoS system have led to a degree of centralization. This centralization occurs because only a few can afford the expensive hardware /collatoral needed to participate.
As a result, it often happens that a small number control a significant portion of the network's hash rate (computational power), which could potentially lead to issues like the 51% attack, where a single entity gains control of the majority of the network.
Network Congestion and Fees: When a blockchain network becomes congested due to a large number of transactions waiting to be processed, transaction fees can skyrocket. This is because users are willing to pay more to have their transactions processed faster. High fees can make blockchain transactions impractical for small or everyday transactions, limiting the technology's utility for broader financial applications such as micropayments.
Liquidity Problems: A major issue in blockchain is that money is often spread across different networks. Unlike traditional finance, where everything is connected, blockchain networks usually work in isolation. This makes it hard to move assets between platforms quickly and safely.
This makes is a lot harder to trade, as fees can go up, and users might not be able to withdraw or swap assets when many people are doing the same. Until blockchains can work better together, this will continue to limit how useful and scalable the technology is.
However, all these challenges still do not describe the main problem that needs to be solved.
After years of peeling back layers from many different blockchains we stumbled upon a common problem that all of them want to solve. Are you ready for it? The root problem these blockchains try to solve is:
Immutable verifiable data.
Dive deep enough and that’s what it all boils down to; unchangeable, trustworthy data & information. Every blockchain exists with the goal to send data from one party to the next in a way that makes sure people can’t alter it.
Bitcoin? Data transfer. Ethereum? Data transfer. Every other blockchain? Yes, you guessed it…Data transfer.
Here you can see a GIF of me connecting all the dots to give you this amazing content
Data transfer is nothing new. We’ve been doing that since the birth of the internet. Moving data from one spot to another. The big difference between Web 2.0 (which is the current internet we’re using) and Web 3.0 (which is the internet we will be using) is this: Web 2.0 involves centralized data storage and control by service providers, using standard protocols.
This while Web 3.0 aims to move towards a decentralized, blockchain-based data management, emphasizing user control, enhanced security, and interoperability. This new structure will allow it to store value on the internet. Decentralized systems where all participants have access to the same information will revolutionize data and value.
This will enable a future where we know where the data came from.
1.1 Why is Web 3.0 going to win from Web 2.0?
After years of thinking we believe the answer as to why Web 3.0 will take over is rather simple. Verified data simply offers greater accuracy, reliability, and compliance, which are crucial for trust, decision-making, and maintaining a good reputation.
Unverified data, on the other hand, carries risks of inaccuracies, misinformation, and potential non-compliance with regulations.
Imagine navigating a city: one guide uses a current, accurate map (verified data), while another uses an old, possibly incorrect map (unverified data). Trusting the guide with the accurate map ensures a safer, more reliable journey, much like relying on a company with verified data.
We reckon most people are smart enough to choose verified data over unverified data. This is the primary reason we believe the transition to Web 3.0 will be inevitable.
So which structure is better at creating verifiable data?
2. Blockchain VS DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)
A blockchain or Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) serves as the foundational infrastructure. The goal of these systems is so other people can build decentralized applications (dApps) on them. You could compare blockchain and DAGs to the land we build our buildings on.
The ground of any piece of land we decide to build on needs to have certain properties before we can start building. The same principle applies to blockchains/DAGs. They need to be able to handle certain things before we can call them a good blockchain or DAG.
So dApps can be thought of as digital businesses built on top of this secure and transparent infrastructure, utilizing its capabilities to create innovative and decentralized solutions.
The difference between a blockchain and a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) lies primarily in their structure and how they process data and transactions.
Let’s first look at the characteristics of a blockchain network:
Linear Structure: A blockchain is a series of blocks linked in a linear, chronological order. Each block contains a list of transactions. Once a block reaches its capacity, a new block is created and linked to the previous one, forming a chain.
Consensus Mechanism: Blockchains typically use consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions. In PoW, for example, miners solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and create new blocks. We won’t be diving too deep into this because there have been countless articles written about this on the web. Which, by the way, is also a big lesson we learned as we grew older…you don’t need to know everything in the details. Sometimes surface level knowledge is enough. Life is too short to learn the details about everything.
Transaction Processing: Transactions are processed in the order they are received, and each block must be verified by the network before the next block is added. This sequential processing can lead to slower transaction speeds, especially on networks with high transaction volumes.
Energy Consumption: PoW blockchains, in particular, are known for their high energy consumption due to the computational power required for mining. Yes we know there are newer blockchains like Kaspa ($Kas) that kind of solved it. But we are not satisfied with better than worse. We are looking for greatness.
That’s how we stumbled upon Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG). Unlike blockchains a DAG has:
Graph Structure: Unlike a blockchain, a DAG doesn't organize transactions into blocks or follow a linear sequence. Instead, it's a graph where each transaction is directly linked to one or more previous transactions. This structure resembles a web or network.
Transaction Validation: In a DAG, each new transaction validates one or more previous transactions. This means that the more transactions added to the network, the faster and more secure the validation process becomes.
Parallel Processing: Because of its non-linear structure, a DAG can process transactions in parallel, significantly increasing transaction speed and scalability.
Energy Efficiency: DAGs typically require less computational power than blockchains, as they don't rely on traditional mining for transaction validation. This makes them more energy-efficient.
2.1 What does Constellation use?
Constellation uses a DAG-based architecture. This choice allows Constellation to address some of the inherent limitations of traditional blockchains, particularly in terms of scalability and speed. By leveraging the DAG structure, Constellation can process transactions more rapidly and efficiently, making it well-suited for handling high volumes of data and transactions. They’ve created a system that gets faster the more it is used. To summarize, Constellation's use of DAG technology represents an innovative approach in the evolving landscape of blockchain and distributed ledger technologies.
3. The famous blockchain trilemma
If you’ve been in the space for a while you’ve probably heard people saying that there is a blockchain trilemma.
So what are the 3 properties which people claim can’t all work together?
Decentralization: This refers to the distribution of control and decision-making across a wide range of nodes or participants, rather than having a centralized authority. Decentralization is crucial for ensuring that no single entity has too much control over the network, which enhances security and resistance to censorship.
Security: This involves protecting the network from various types of attacks and ensuring the integrity and continuity of the blockchain. A secure blockchain is one where transactions are reliably recorded, and the history of transactions cannot be altered without detection.
Scalability: This is about the ability of the blockchain to handle a large number of transactions quickly and efficiently. Scalability is essential for widespread adoption, as it ensures that the blockchain can support a high volume of transactions without significant delays or increased costs.
A trilemma suggests that it is extremely challenging to achieve all three properties simultaneously to their fullest extent.
For example, a blockchain might achieve high decentralization and strong security, but at the cost of scalability (as seen in Bitcoin and Ethereum's early versions). Alternatively, increasing scalability might require compromises in decentralization or security.
This has been the narrative for years! “Solving the trilemma is impossible!”
Luckily there are people out there who understand that something being impossible now, doesn’t mean it’s impossible in the future. I mean for crying out loud, we have airplanes. I can bet that the people that told everybody that one day we would fly in the sky in metal airplanes we’re looked at as weird, delusional individuals. Yet here we are.
The same principles apply to the trilemma. People looked at the problem and instead of seeing a dead end, they came up with better solutions.
But it gets even better.
Imagine discovering that besides the trilemma there are actually 5 problems that need to be solved. A so called quinlemma! A term invented by Wyatt Meldman-Floch, ex CTO of Constellation.
Imagine seeing many different chains boasting about solving 2 of the 3 problems, totally unaware of the other 2 problems that they will encounter. This is where being short sighted gets you. It’s a game of the blind leading the blind.
So what are these other 2 problems that most will encounter later on?
3.1 Interoperability & Composability
Sound the alarm! We have big words! Don’t worry we got you. Let’s first dive into interoperability.
Interoperability in the context of blockchain technology, including networks like Constellation, is a crucial feature that allows different blockchain and legacy systems to communicate and interact with each other seamlessly.
It's about creating a fluid exchange of information and value across diverse blockchain networks and between blockchain and traditional systems. To understand this better, let's draw an analogy with the evolution of the internet, particularly the transition from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0.
3.1.1 Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 Analogy:
Web 1.0: This was the early stage of the internet, often referred to as the "read-only" web. Websites were static, and interaction was limited. Users could consume content but had limited ability to create or interact with it. There was little to no interoperability between different web platforms; each website functioned as an isolated island.
Web 2.0: This is the current version of the internet, often called the "read-write" web. It's characterized by interactivity, social networking, and user-generated content. Websites and applications in Web 2.0 can interact with each other through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), sharing data and functionalities. This interoperability has led to a more integrated and dynamic internet experience, where services like social media, e-commerce, and online collaboration tools can seamlessly connect and interact.
3.1.2 Blockchain Interoperability:
In the blockchain world, interoperability is akin to the leap from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0. Early blockchain networks operated in silos, similar to Web 1.0 websites. Each blockchain had its own rules, protocols, and use cases, and there was limited ability for these blockchains to communicate or share information.
Interoperability in blockchain aims to break down these silos, allowing different blockchain networks to interact. This means a user or application on one blockchain can seamlessly access and utilize data or assets on another blockchain. For example, a smart contract on Ethereum could trigger a transaction on the Constellation network, or a digital asset like a token could move between different blockchains without the need for a centralized exchange.
3.1.3 Constellation and Interoperability:
Constellation addresses interoperability by creating a network that can connect with various data types and protocols, not just within the blockchain ecosystem but also with traditional systems. This approach is similar to how Web 2.0 applications can interact across different platforms and with older web technologies. By doing so, Constellation aims to facilitate a more integrated and efficient blockchain environment, where the transfer of information and value can occur across different blockchain networks and between blockchain and non-blockchain systems. Okay that should cover interoperability! Time to move on to composability.
3.2 What is composability?
Composability in the context of blockchain technology refers to the ability to combine and recombine different components and services in a modular and flexible way. It's about creating systems where individual parts can be used interchangeably and integrated seamlessly to build new applications or services. To understand this concept better, let's use an analogy related to LEGO bricks.
Imagine each blockchain service or application as a LEGO brick. In a non-composable environment (like using different types of building blocks that don’t fit together), you're limited to what you can build with each type of brick. You might have a set of LEGOs, wooden blocks, and K'NEX, but since they don't connect with each other, your creative possibilities are limited.
In a composable blockchain environment, it's like having all your building blocks designed like LEGOs. Each piece can easily connect with others, regardless of their original set or purpose. This means you can take a piece from a LEGO spaceship set, connect it with pieces from a LEGO castle set, and create something entirely new and functional. The ease of combining these diverse pieces encourages innovation and creativity.
Constellation's approach to blockchain technology embraces this concept of composability. By providing a flexible and interoperable framework, it allows for various applications and services to be easily integrated and recombined. This capability is crucial for fostering a dynamic and innovative blockchain ecosystem, where new solutions can be developed rapidly by leveraging existing components.
If you came this far, congratulations! You now have a clear understanding of the foundation of these new systems. This will serve as a great guide when people try to sell you on why their blockchain or DAG is the best. If they’ve not solved all of these problems, than the chance of mass adoption for them decreases dramatically.
4. Consensus: A formal agreement
If you’re not familiar with the space you’re probably wondering what’s up with all these difficult words. We've all been there. Over the years you see the words so many times that they simply become part of you. So don’t worry if you don’t understand it yet. You will as time goes on.
Consensus, in the context of blockchains and Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), is the mechanism by which the network agrees on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the ledger. It ensures that all participants in the network have a consistent view of the blockchain's history. Two common consensus mechanisms are:
Proof of Work (PoW): In PoW, participants (miners) compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first one to solve it gets the right to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. This process is energy-intensive but secure.
Proof of Stake (PoS): In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" as collateral. It's more energy-efficient than PoW but relies on participants having a vested interest in the network's security.
Consensus ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the state of the ledger, preventing double-spending and maintaining the integrity of the blockchain or DAG. Different blockchain and DAG platforms may use variations of these consensus mechanisms or entirely different ones, each with its own trade-offs in terms of security, scalability, and energy efficiency.
4.1 Which consensus does Constellation use?
Constellation Network employs a unique consensus mechanism known as "Proof of Reputable Observation" (PRO). This mechanism is distinct from more traditional consensus models like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), commonly used in other blockchain systems. Let's delve into what makes PRO unique:
Proof of Reputable Observation (PRO):
Reputation-Based: In PRO, the consensus is achieved not just through the validation of transactions but also based on the reputation of the nodes participating in the network. Nodes are assigned a reputation score based on various factors, including their history of transactions and validations. This score influences their role and weight in the consensus process.
Observation and Validation: Nodes in the Constellation network observe and validate transactions. However, unlike traditional consensus mechanisms where every node has to agree on every transaction, PRO allows for a more streamlined process. Nodes validate transactions based on their observation and the network's overall state, making the process more efficient.
Scalability and Efficiency: One of the key advantages of PRO is its scalability. Since the mechanism doesn't require every transaction to be validated by every node, it significantly reduces the computational load and allows for faster processing of transactions. This makes the Constellation network highly scalable and capable of handling large volumes of transactions.
Security Through Decentralization: The reputation-based system ensures that nodes have a vested interest in maintaining the integrity of the network. Nodes with higher reputations have more to lose if they act maliciously. This setup promotes a secure and decentralized network, as it discourages bad actors and rewards those contributing positively to the network.
Energy Efficiency: Unlike PoW, which requires extensive computational power and energy, PRO is much more energy-efficient. This efficiency stems from its streamlined validation process and the absence of computationally intensive tasks like mining.
Adaptability: PRO allows for a dynamic and adaptable network. The reputation scores can change over time based on nodes' behavior, allowing the network to evolve and respond to changing conditions and requirements.
To summarize Constellation's Proof of Reputable Observation consensus mechanism offers a unique blend of efficiency, scalability, and security. By leveraging a reputation-based system, it ensures that the network remains secure and decentralized, while also addressing some of the key limitations of traditional blockchain consensus mechanisms, such as high energy consumption and limited scalability. This innovative approach positions Constellation as a forward-thinking player in the blockchain space, capable of supporting complex and high-volume data transactions.
5. Real world applications of DAG technology
This is probably the most exciting part. You can talk a lot, but after a while you have to back up your words with evidence. This is where Constellation really outperformed the entire space. In 2021, Constellation acquired the multimillion dollar SaaS startup Dor to scale blockchain technology to more than 2,000 retailers. Game changer! And it does not stop there. We will also dive into Digital Evidence, a powerful solution that brings tamper proof, court ready data to emergency services, law enforcement, and more.
5.1 So what is Dôr Traffic Miner?
The Dôr Traffic Miner is an innovative device that blends the physical and digital realms, specifically designed for retail and physical business spaces. It's a people-counting hardware tool that can be installed at the entrances of stores, restaurants, or any similar establishments. This device's primary function is to track the number of people entering and exiting, providing businesses with critical data on foot traffic patterns.
What makes the Dôr Traffic Miner stand out is its integration with blockchain technology. This integration ensures that the data collected is not only secure and transparent but also immutable. Additionally, businesses using this device are incentivized through cryptocurrency rewards, offering them a novel way to earn from sharing their foot traffic data.
And which problem does it solve?
The problem that Dôr Traffic Miner aims to solve is multifaceted. In the retail sector, understanding customer behavior and store performance is a significant challenge. By providing accurate data on foot traffic, businesses can gain insights into customer engagement levels, conversion rates, and overall store effectiveness.
This information is invaluable for optimizing store operations, including staffing, inventory management, and marketing strategies. Furthermore, the Dôr Traffic Miner addresses the growing need for data security in the age of big data. By leveraging blockchain, it ensures that the collected data is protected against tampering and breaches.
Lastly, by linking a tangible, real-world device with the digital world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, the Dôr Traffic Miner encourages businesses to engage with and adopt blockchain technology, showcasing its practical applications beyond the digital sphere.
This will be the first of many applications that we be built on top of the Constellation network. As time goes on we will talk about more and more, so be sure to subscribe so you don’t miss detailed explanations of the future of Constellation.
If you’re not sold yet we don’t know what to tell you. Creating and rereading this only sold me more on the unique value proposition of Constellation $DAG.
5.2 How Constellation Is Securing Digital Evidence with Blockchain
Picture this: a police officer on-site records crucial data. Or a fire department documents the cause of a blaze. What if all that information from video, audio or GPS, reports could be 100% trusted and legally valid? No file corruption, no questions about authenticity?
That’s exactly what Constellation Network is tackling with Digital Evidence.
What is Digital Evidence?
Digital Evidence is a smart blockchain solution that locks down evidence in a way that is unchangeable and court-ready. Data collected from police cars, bodycams, fire trucks, or EMS devices is recorded on Constellation’s Hypergraph.
The result? Data you can trust. No tampering. No doubts.
Panasonic TOUGHBOOK + Blockchain = Power Move
Together with Panasonic, Constellation has created a powerhouse solution: Digital Evidence is built right into Panasonic’s rugged TOUGHBOOK devices. These are already widely used by first responders, so there’s no need for new hardware. Just plug in and go.
Why it matters
Proof stays proof
Once data is captured, it stays exactly as it was. No alterations.Legally admissible
Blockchain ensures the integrity of the data, making it strong enough to stand up in court.Smart Checkmark certification
Organizations using Digital Evidence earn a certification that proves they follow transparent, secure data practices.
Beyond emergency services
This isn’t just for police or firefighters. Digital Evidence is making waves in other industries too:
AI data verification
Ensure training datasets for machine learning are clean, accurate, and untouched.Retail analytics
In partnership with Dor Technologies, they’re collecting and securing in-store foot traffic data. Great for insights, safe for privacy.Intellectual property protection
Need to prove ownership or originality? Store it immutably on-chain.
What’s next? Even smarter integration
Constellation plans to take Digital Evidence even further — with integrations into AI platforms, business intelligence tools, and government systems. The goal: bulletproof, verifiable data you can use anywhere.
6. Enter Delegated Staking: A Game-Changer for DAG Holders
Constellation’s innovation keeps moving forward, and their latest rollout, Delegated Staking, is a perfect example. Until now, taking part in the Constellation network meant either holding $DAG or running a node, which requires quite a bit of technical skill and commitment. With Delegated Staking, anyone can now support the network and earn passive income, no tech expertise needed.
This feature makes staking rewards accessible to everyone by allowing $DAG holders to delegate their tokens to trusted validator nodes. You remain in control of your funds, while your chosen validator handles the technical side. It’s staking made simple.
6.1 How It Works (In Plain English)
Getting started with Delegated Staking is refreshingly simple:
Download the Stargazer Wallet – your command center for everything DAG. https://constellationnetwork.io/stargazer-wallet/
Head over to the DAG Explorer and connect your wallet.
https://mainnet.dagexplorer.io/stakingPick a validator – choose based on performance, reputation, and fees (between 5–10%). There’s a validator called The Sharepot, if you enjoy(ed) our content we would be really grateful if you delegate to this node. We’re partnering with them and our plan is to redistribute some of the rewards to people who stake to that validator as a way to give back to the community and incentivize long-term support.
Stake your $DAG – a minimum of 5,000 $DAG is required. You can stake to up to 10 validators at once.
Sit back and earn – rewards are distributed regularly. If you want to move your stake, you can easily switch between different validators. Want to stop staking altogether? You can unstake your tokens, which starts a 21-day unbonding period. During this time, your tokens are locked and not earning rewards, but once the period ends, they’re fully available again.
6.2 Why It Matters
This is more than just a new feature. It marks a major step forward in how the Constellation ecosystem empowers its community. Delegated Staking helps strengthen the network's decentralization while giving more people the chance to benefit from its growth. You can earn rewards, help secure the network, and support the wider adoption of DAG and Layer 0 infrastructure.
Simply put, you no longer need to be a tech expert to get involved.
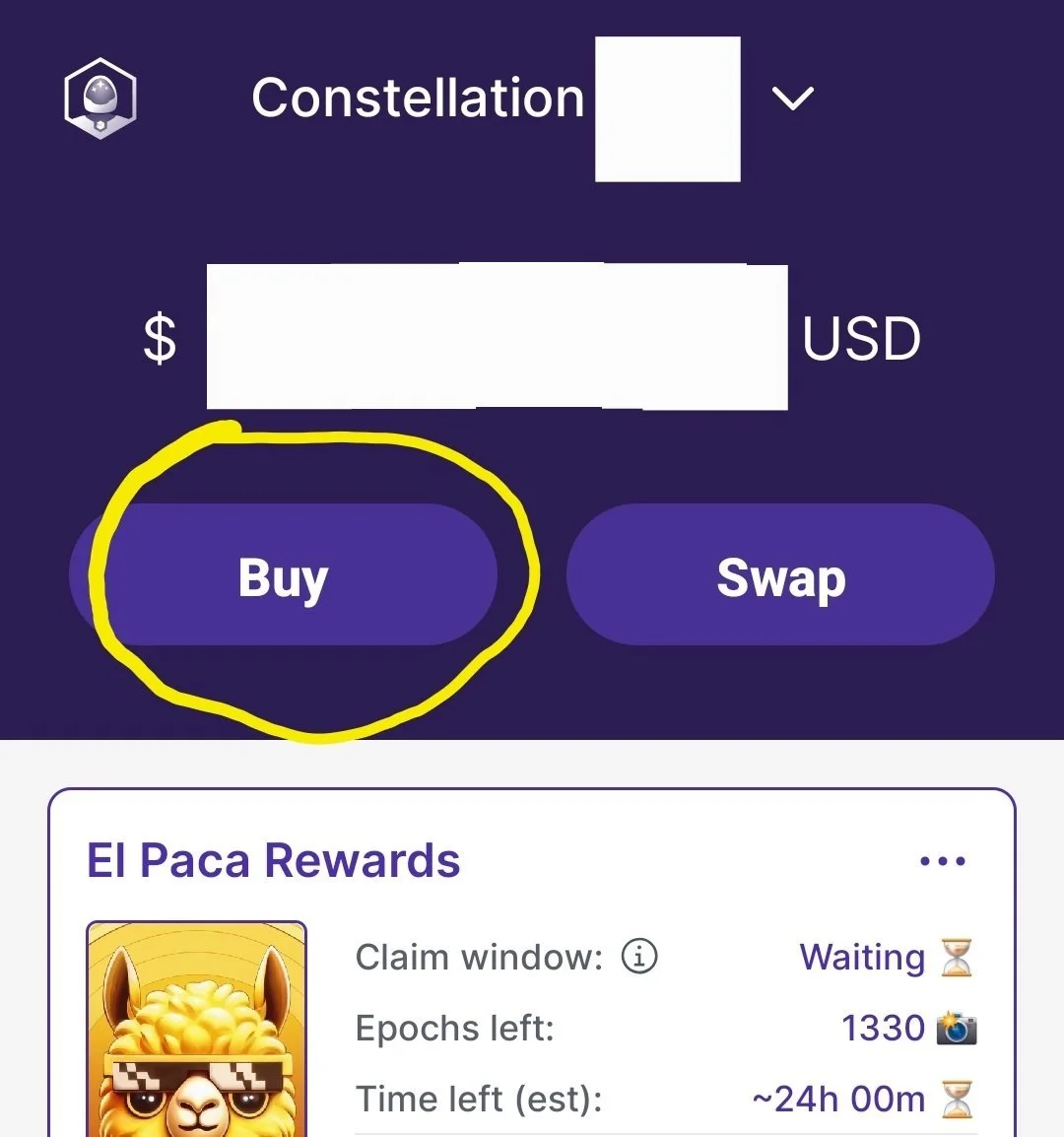
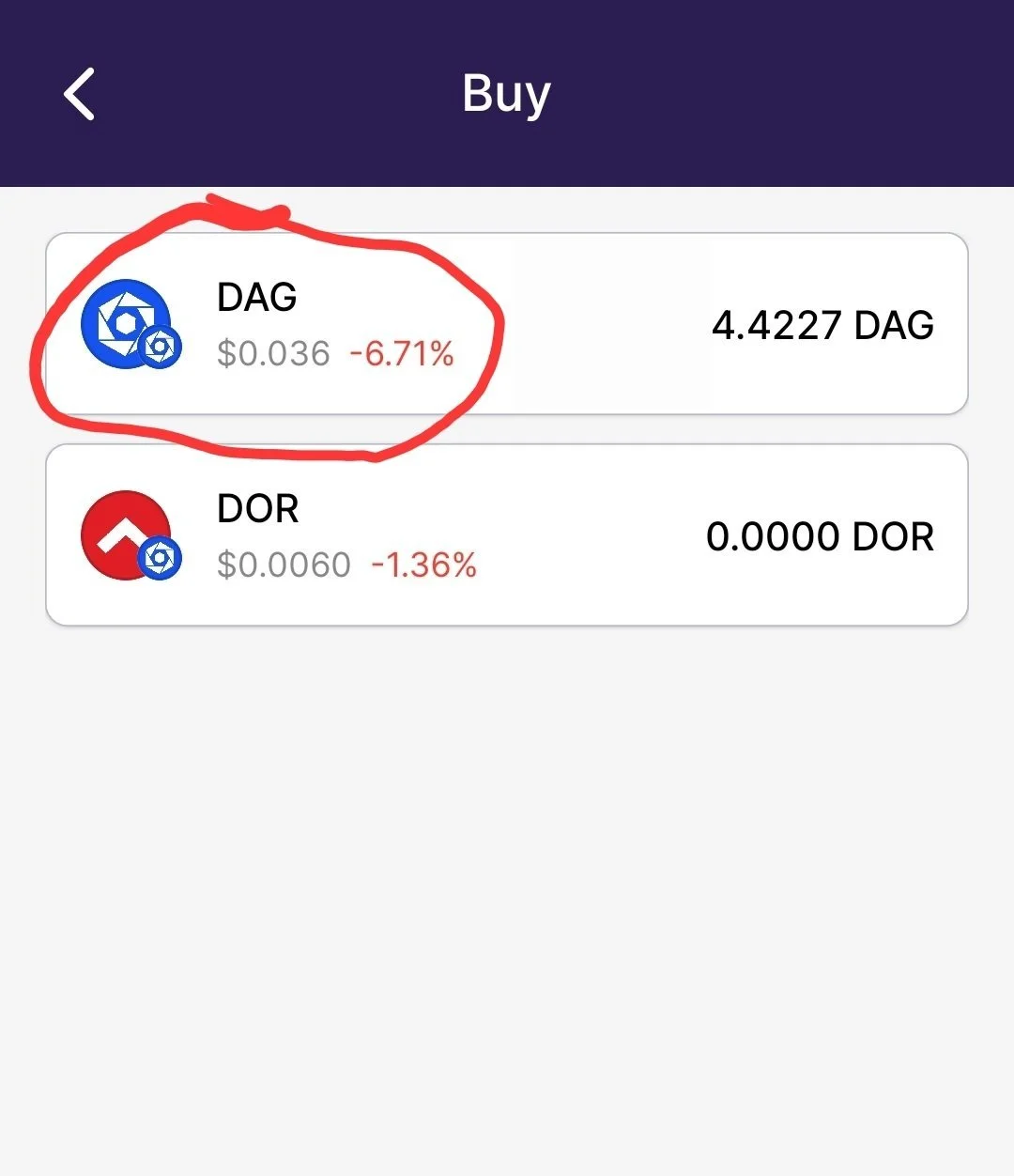
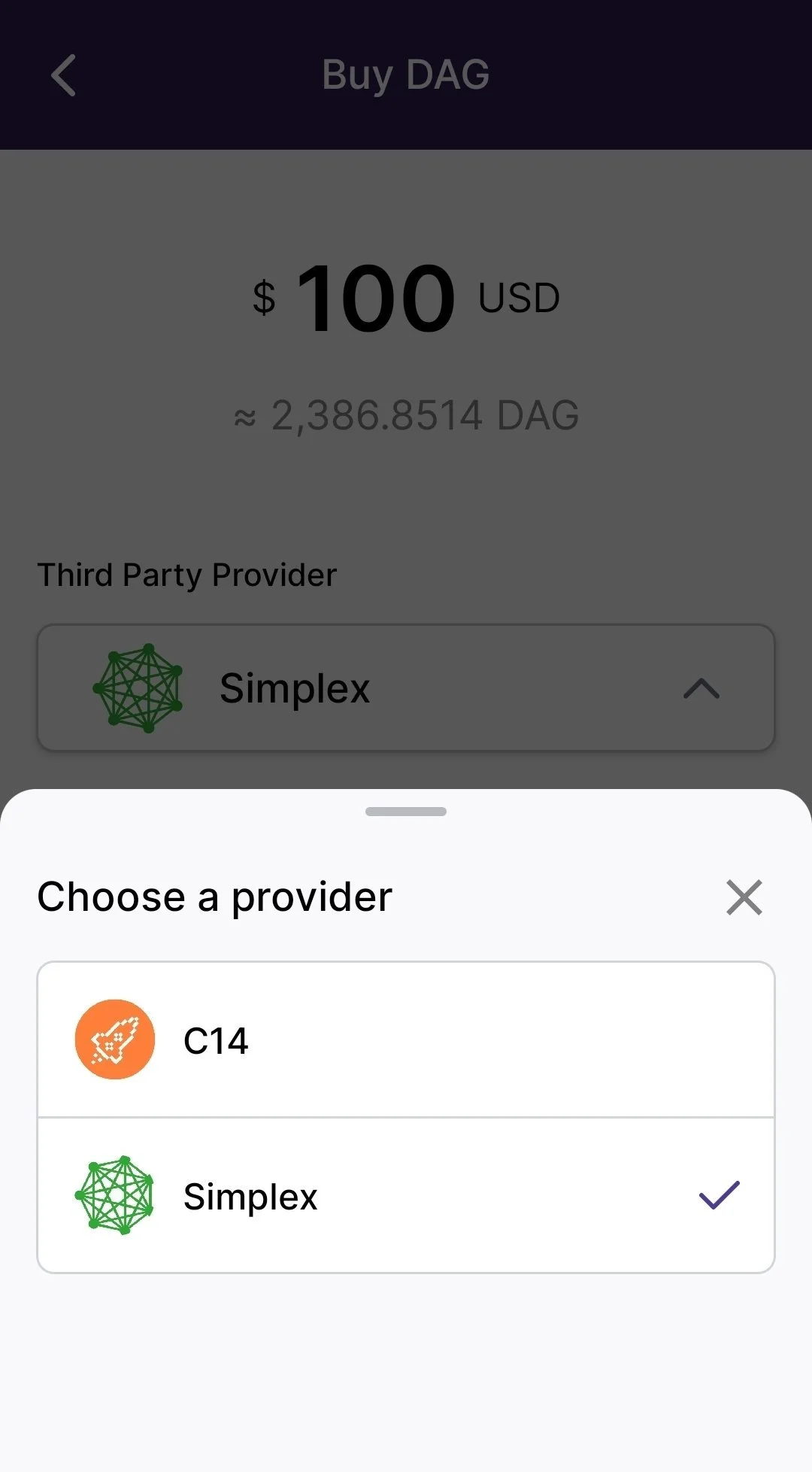
7. How to buy Constellation $Dag
7.1 Through the Stargazer Wallet
Buying $DAG is simple and seamless with the Stargazer Wallet. Just start by heading to the official Constellation Network website and downloading the Stargazer Wallet app on your phone, laptop or desktop.
Once it’s installed, you can buy $DAG right from the app using your credit card. No extra steps or exchanges needed. Here’s how:
Download/Open the app and either create a new wallet or import an existing one.
Tap “Buy DAG” and select your preferred payment method (like a credit card).
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete your purchase safely and securely.
Keep in mind: your first transaction might take 1–2 days to process while everything gets verified. After that, future purchases are usually much quicker.
7.2 On the Kucoin exchange
Step 1: Create a KuCoin Account
Visit KuCoin Website: Go to KuCoin's official website.
Sign Up: Click on the 'Sign Up' button and fill in your email address and password. Follow the instructions to complete the registration process.
Verify Your Account: Complete the necessary KYC (Know Your Customer) verification for enhanced security and higher transaction limits.
Step 2: Fund Your Account
Log In: Access your KuCoin account using your credentials.
Deposit Funds: Navigate to the 'Assets' or 'Deposit' section. You can deposit either fiat currency (like USD, EUR) or cryptocurrency (like BTC, ETH) depending on your preference and the available options on KuCoin.
Choose Deposit Type: Select the type of currency you want to deposit.
Transfer Funds: Follow the instructions to transfer funds from your bank account or another wallet to your KuCoin account.
Step 3: Buy $DAG
Go to the Trading Section: Once your account is funded, navigate to the 'Markets' or 'Trade' section on KuCoin. Note: Kucoin has a Funding and a Trading place. When you deposit funds on Kucoin they’ll innitially be placed in your “Funding” account. To trade coins you need to transfer the coins from your Funding account into your Trading account.
Select the Trading Pair: Look for the $DAG trading pair that matches your deposited currency (e.g., DAG/USDT, DAG/BTC).
Place an Order: Choose between a 'Market' order (to buy at the current market price) or a 'Limit' order (to set a price at which you want to buy). Enter the amount of $DAG you wish to purchase. Market orders are bought right away, while Limit orders are only bought when the price of the coin reaches the price you’ve placed in the order. For beginnners and long-term holders we recommend the Market order.
Review and Confirm: Double-check the details of your order and confirm the purchase.
Step 4: Secure Your Tokens
Transfer to a Wallet: For added security, consider transferring your $DAG tokens to a personal, external wallet, especially if you're planning on holding them long-term.
Choose a Wallet: Select a wallet that supports $DAG tokens. We’re a big fan of the Stargazer Wallet from Constellation.
Withdraw from KuCoin: Go back to the 'Assets' section on KuCoin, click on the $DAG coin, select 'Withdraw,' and follow the instructions to transfer your $DAG tokens to your chosen wallet.
Additional Tips
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with any changes or updates on KuCoin's platform.
Security: Always use strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your KuCoin account.
Fees: Be aware of transaction fees for deposits, withdrawals, and trading on KuCoin.
Remember, the value of cryptocurrencies can fluctuate widely, and trading them can be risky. It's important to only invest what you can afford to lose.
8. I am a developer, where should I start?
Some people use tech. Others build it. Just like the App Store or Google Play would be useless without developers uploading their apps, the Constellation Network needs builders to grow and thrive.
If you're ready to build on Constellation, here are a few resources to help you get started:
YouTube Playlist – Start Here
These videos will give you a solid understanding of what’s possible and how to get going:
👉 Constellation YouTube Playlist with 9 videos to get you started.
GitHub – Metagraph Examples
The official metagraph-examples repo includes practical use cases you can explore and build from.
A lot of people used these as a "copypasta" foundation during last year’s hackathon (hey, no shame – it works!).
These examples are built to help you understand and apply different features of the Euclid SDK, Constellation’s framework for building decentralized applications.
Pro Tip: Don’t just jump into the code. First, take time to understand how the Constellation network works, what a Metagraph is (we’ll explain what this is in the future but for now you can find more information about Metagraphs here: https://docs.constellationnetwork.io/network-intro/what-is-a-metagraph), and how the Euclid SDK empowers scalable, secure, decentralized development.
9. The end
If you made it this far you are the real warrior. I remember reading long articles on other websites over the years. I know most people will skip anything longer than a tweet. But then there are people like you and I who really take a deep dive into the technology. We build fundamental knowlegde which will help us see FUD and misinformation. Fundamental knowlegde that’s meant to last a lifetime. Constellation Network represents not just a unique investment opportunity but also a transformative platform poised to significantly evolve and reshape the blockchain space.
Investing in Constellation is not just about capitalizing on a unique financial opportunity; it's about being part of a pioneering movement that is set to redefine the boundaries of blockchain technology. Its innovative approach and practical applications position Constellation as a key player in driving the next wave of blockchain evolution, making it an exciting and promising platform for anyone looking to be at the forefront of this technological evolution.
Viva la evolución🔥